 Back to all articles
Back to all articles
Blogs
Automated CI/CD Pipeline: Implementation Best Practices for US Startups

T ech evolves quickly, and businesses that stand out are the ones that release updates rapidly and fix issues just as fast. Automated CI/CD pipelines speed up the build process, reduce deployment risks, and help teams keep up with user expectations.
Research from DORA’s State of DevOps showed that high-performing teams highly rely on CI/CD automation to maintain faster and reliable product delivery without compromising on quality.
Additionally, for startups competing in today’s rapidly moving tech world, every commit and deployment plays an important role in shaping the product’s trajectory. That’s why automation isn’t just a DevOps task; it is a key strategy for scaling efficiently.
In this blog, we’ll explore everything you need to know about automated CI/CD pipelines, from basic mechanics to best implementation practices.
Explaining CI/CD Pipeline
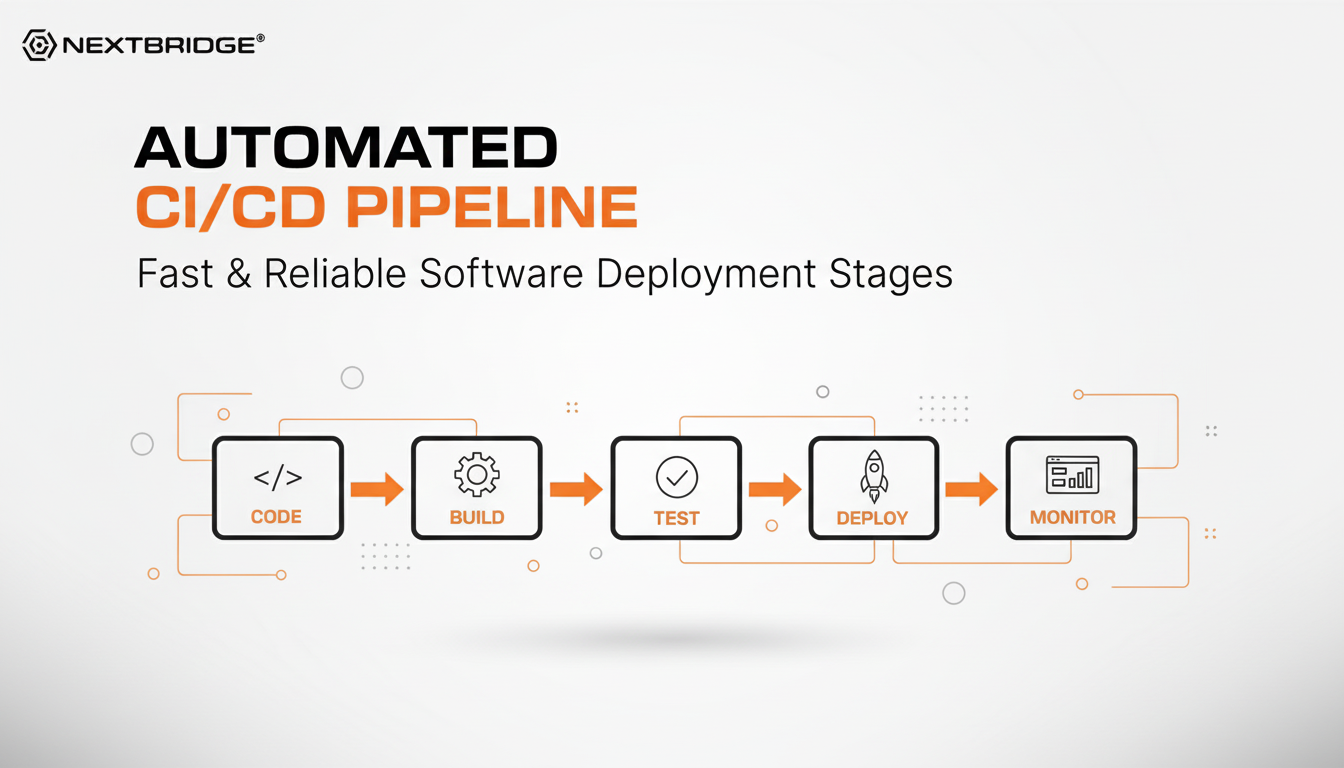
As defined, a modern CI/CD pipeline is an automated build process that helps you move code through every stage of development, from writing to deploying it. In simple terms, it is a series of automated steps, such as continuous integration, automated testing, and deployment, that simplify the software delivery.
Instead of doing everything manually, the pipeline handles the entire build, test, and release processes automatically.
Importance for US Startups
But what does make it essential for startups? The tech market in the US is evolving at lightning speed, which highlights the demand for automation, one of the key characteristics of this pipeline. This gives startups a clear advantage in making software delivery quicker, safer, and more efficient.
For instance, the automated pipeline helps in faster releases, such as new updates and features, reach users quickly, keeping your product at the top. Moreover, it also reduces human errors and bugs, resulting in a higher quality release.
Developers spend less time on manual tasks and more on building something unique, which reduces engineering overhead. Last but not least, whether you’re making a SaaS, AI, fintech, or mobile app, automated pipelines help in growth without slowing your team down.
In the next sections, we will discuss the key components and stages of the automated pipeline to understand the workflow better.
What are the Core Components of CI/CD Automation?

The modern automated CI/CD architecture consists of the following elements to make the software delivery faster and reliable.
- Continuous Integration (CI): The first important element, and from where the process starts, is continuous integration (CI), which means that developer can continuously add their code to a shared branch.
Every time changes are made to code, or a new one is added, the system automatically runs checks across build, test, and release. This helps the team to flag errors or vbuys early and avoid any merge conflicts.
- Continuous Delivery: This part of the process ensures that every change to the code is always ready to be deployed. After automated builds and tests, the code is prepared for release. However, the deployment to production is triggered manually.
- Continuous Deployment: The CD in the pipeline stands for continuous deployment, which takes automation one step further. Every code change that passes through a series of pre-defined testing is automatically deployed to production without manual intervention.
Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment: A Quick Glance
Although both of them extend automation beyond continuous integration and are used interchangeably, they have distinct purposes.
| Aspect | Continuous Delivery | Continuous Deployment |
| Deployment Trigger | Manual approval before release | Automatically release changes |
| Goal | Ensure code is always ready to deploy | Automatically release every change that passes tests |
| Risk Control | Higher control over timing | Quick release but requires rigorous testing |
| Use Case | Startups or teams that demand scheduled releases | Teams requiring rapid changes and quick user feedback |
How Does An Effective Pipeline Work? Key Stages
A strong CI/CD architecture has several stages that help code move smoothly from development to production. Here’s how each step works:
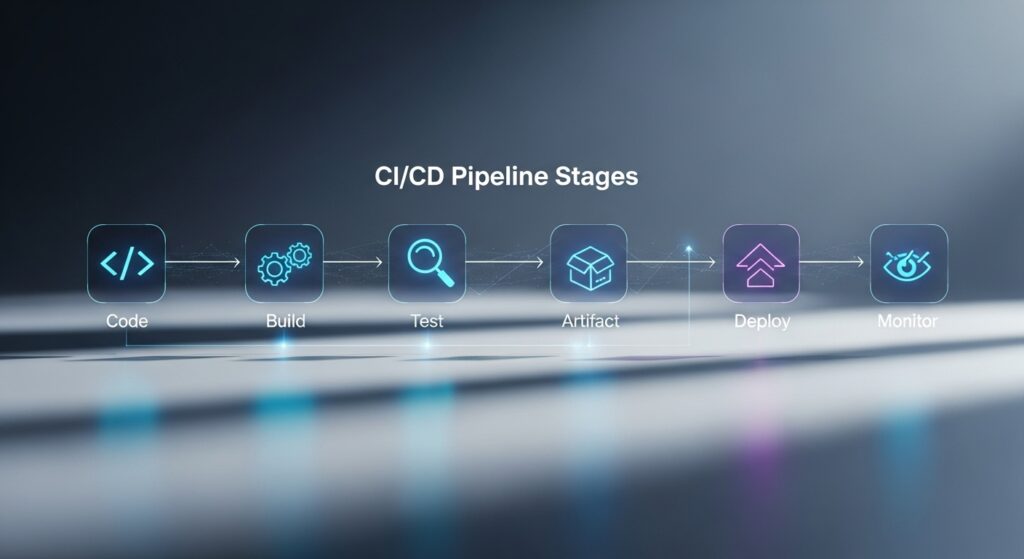
1. Code & Version Stage: Where Everything Starts
In this stage, developers keep their code in a shared repo such as Git. This makes it easier for teams to track changes and work at the same pace. Moreover, branches and pull requests are also created here to keep the code clean and avoid conflicts.
2. Build Stage: Turn Code Into Reality
When the code changes, the pipeline itself builds the application and makes it ready for testing.
This step helps find errors early and ensures the code is always ready to deploy.
3. Testing Stage: Catch Problems Before the Users Do
Here, the pipeline runs different tests, such as unit, integration, and end-to-end, to double-check the code. The goal of this stage is simple: find bugs early so they never make it to production and deployment.
4. Artifact Management Stage: Store It, Track It
After the code is built and tested, the output files are saved securely for deployment. At this phase, the pipeline manages versions and organizes them properly. This makes releases more predictable and allows easy rollbacks when needed.
5. Deploy Automatically, Monitor Continuously, Sleep Peacefully
After passing every step, the code is automatically deployed to the production or staging environment. This stage also includes continuous monitoring to track performance, identify issues, and allow for quick rollbacks to guarantee a stable and secure release.
A Quick Overview of Different Types of Automated Testing
Here are the most common types of testing carried out throughout an automated pipeline:
- Unit Testing: Used to test separate pieces of code, such as functions or methods. This makes sure that each small part works accurately before being combined with others.
- Integration Testing: Analyze how several services or modules work together. It helps detect issues that arise when connected components interact.
- End-to-End: Initiate real user workflow, from login to completing the key action. It is used to confirm that the entire application works as expected from start to finish.
- API Testing: Confirm the behavior, accuracy, and responsiveness of APIs to make sure that backend services interact correctly and return the expected results.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate speed, load handling, and responsiveness to check bottlenecks and ensure the system performs well under stress.
- Security Testing: It is run to find out errors, misconfigurations, and potential attack options, protecting your applications by catching risks early in the pipeline.
Related Read: DevOps Guide and Best Practices
Common CI/CD Challenges for Startups
Before we dig deep into how to execute pipeline automation effectively, here are some common challenges that need careful consideration:
- Slow Pipelines: One of the frequent issues is slower pipelines. For instance, when build and test cycles take too long, developers wait for hours for feedback. These pipelines also slow down productivity, delay feature release, and make it harder to adapt instantly to market needs.
- Tool Overload: Using too many tools can overload the workflows and increase maintenance overhead. Startups may struggle to select the best pipeline automation tools, integration, training, and extra costs while trying to keep the pipeline efficient and running.
- Flasky Tests: Apart from slow pipelines, tests that fail inconsistently create confusion and remove trust in the pipeline. Developers spend time finding false failures rather than focusing on building unique features.
- Unclear Branching Strategies: The other significant issue is undefined branching rules, resulting in merge conflicts and inconsistent releases. Unclear branching also causes the team to lose track of changes, making deployment riskier.
Practical Strategies to Implement Automation in CI/CD
In order to carefully and efficiently add automation, you need to adhere to the following strategies and techniques:
Start Simple: Don’t Overcomplicate
The first basic rule is to start with a very minimal pipeline. Your focus should just be on building, testing, and deploying. Why? A simple pipeline works faster, gives quick feedback, and is easier to manage. Moreover, once you feel that your team is growing, then gradually add stages like integration tests, performance tests, or additional test environments.
Create Different Setups with IaC
Use code tools like Terraform, Ansible, or CloudFormation to set up your environments. Through this, you can confirm that your development, staging, and production environments are consistent. Plus, creating different setups also simplifies scaling, onboarding, and disaster recovery.
Speed Up Delivery with Parallel Testing & Catching
When your team becomes mature, use parallel testing that allows multiple test environments to run concurrently. This makes the pipeline run much faster. Additionally, use a caching technique so that the pipeline doesn’t rebuild or download the same things again and again. Both these techniques help teams give updates faster without compromising quality.
Add Clear Branching & Review Policies
It is important to use simple, clear branching methods (e.g., GitFlow, trunk-based development) and proper code review. This helps reduce merge conflicts and keeps the quality of the code. Furthermore, automated triggers, such as running tests or deploying on pull requests, complement these practices for seamless workflows.
Integrate Security Early (DevSecOps)
One of the key strategies for the smooth implementation of automation is adding security checks. Use automated tools to find errors, detect secrets, and check dependencies.
Moreover, early security interaction limits risks and ensures consistent compliance, builds user trust that is important for fintech, healthcare, and SaaS startups.
Best Practices to Optimize Your Automated CI/CD Pipeline
Ever wondered why some teams deploy confidently while some struggle with every release? Well, the difference usually lies in how well-optimized your pipeline is. Here are some simple yet most effective practices to keep your pipeline running smoothly.
- Keep Your Pipeline in Smaller Segments: The first technique is to break your pipeline into smaller, separate stages. Why? Because in case of one segment failure, you instantly know where and why. Plus, it also makes updates easier, no more reviewing the whole thing in order to fix one step.
- Use Temporary Test Environments: Set up environments only when you need them, and after this, destroy them. This keeps the test clean, removes “it worked on my machine” issues, and narrows down infrastructure costs.
- Track the Metrics That Matter: Don’t do guesswork. Track deployment frequency, lead time, change failure rate, and pipeline duration. Your metrics tell you where your pipeline slows down, where it compromises quality, and where automations should be implemented next.
- Automate Your Rollbacks: Mistakes happen, even automated pipelines run bad code sometimes. Here, quick rollbacks help you and ensure your team can go back to a stable version within seconds.
Some Popular Tools For CI/CD Test Automation
Confused about choosing the right tools that make automation simplified and more scalable for evolving teams? Below are some best pipeline automation platforms and CI CD tools for automation testing, you can rely on:
Testing Tools
| Cypress | Easy-to-use tool for end-to-end web testing. |
| Playwright | Cross-browser testing with strong automation features. |
| Jest | Lightweight JavaScript framework best for unit and integration tests. |
CI/CD Platforms
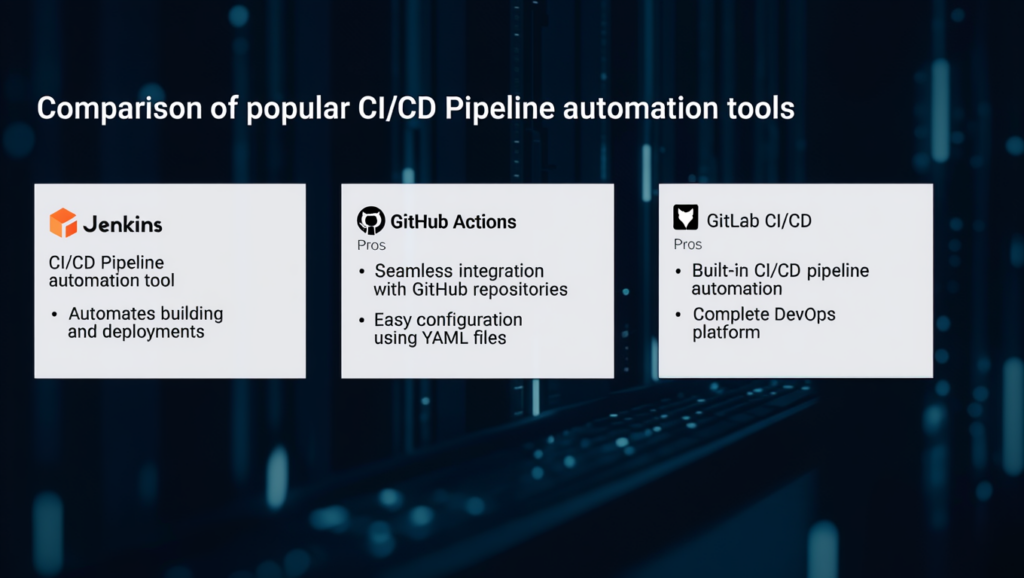
| GitHub Actions | User-friendly, perfect for teams already using GitHub. |
| GitLab CI/CD | Complete platform with pre-built CI/CD, security, and monitoring. |
| Jenkins | Highly adaptable open-source solution. |
| CircleCI | Quick pipelines with advanced optimization features. |
Container & Deployment Tools
| Docker | Packages your app into smooth containers for easy builds and deployment. |
| Kubernetes | Automate deploying, scaling, and handling containerized applications. |
Additionally, we also offer expert services in automation pipelines. With our service, startups don’t just pick tools; we execute them strategically. In short, we create pipelines that save time, reduce errors, and scale with you. So, what are you waiting for? Start building your pipeline with us!
Wrapping Up
In the startup landscape, speed doesn’t wait, and neither should you. A well-designed CI/CD pipeline is what you need to turn every code into a deployment-ready: faster feedback, fewer errors, and risk-free release.
Think of it as your invisible co-founder that manages difficult tasks (testing, building, deploying) while your team focuses on building something big. In conclusion, when you combine the right strategies with the smart data pipeline automation, you can give your startup a space to scale faster, ship confidently, and stay ahead of the competition.
FAQs
How long does CI/CD setup take?
Generally, a basic pipeline can be set up in a few days to several weeks, depending on the complexity and multi-environment pipelines.
Do early-stage teams need automated testing?
Of course! Even small teams take advantage of automated tests to find bugs initially and maintain code quality.
What’s the simplest pipeline to start with?
The best practice is to start with a simple pipeline: build, test, and deploy, then gradually add more stages as your product matures.
Don't hire us right away
talk to our experts first,
Share your challenges, & then decide if we're the right fit for you! Talk to Us
Partnerships & Recognition
Commitment to excellence






