 Back to all articles
Back to all articles
Blogs
A Guide to Know all about Globalization Testing in QA


With the advancement of science and technology, the world has turned into a global village. Countries from different cultures interact and trade with each other. This is the reason why various software applications are being developed to keep different countries connected across the globe. Such software applications are part of a greater agenda known as Globalization Testing.
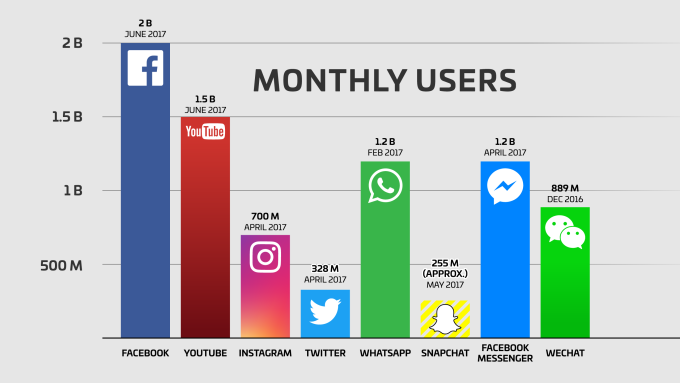
Globalized software is compatible with various topographical conditions and cultures. Over the years the number of people using globalized software is increasing by leaps and bounds. Some examples are Facebook and Twitter i.e. they are compatible with multiple languages and can be used in different locales.
According to the recent stats, the number of monthly active users on Facebook is 2.85 billion. This proves the fact that globalized software is the need of the hour.
To ensure the quality of globalized software, it is first essential to test it properly before launching it. This is achieved by a process known as Globalization Testing. Let’s get acquainted with the concept first.
Everything about Globalization Testing
Globalization Testing is a testing process in which software is examined to ensure that it can be used, globally. It is also called G11N testing. It is divided into the following types:
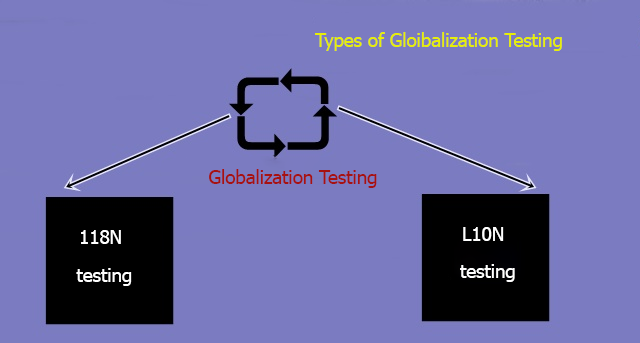
- Internationalization Testing
- Localization Testing
Let’s understand the concepts in depth:
Internationalization Testing
Internationalization Testing is also called I18N testing. This testing is performed to check whether an application is compatible with different languages. In other words, this testing is performed to ensure that an application is capable of handling inputs in different languages. Hence, in this testing, it is ensured that the desired application can be used all across the world.
There are three main purposes of executing this sort testing:
- To ensure that the application displays the right language
- To ensure that the alignment of the content displayed is correct
- To ascertain that the content displayed by the application has no errors
Localization Testing
Localization Testing is also called L10N testing. This testing is done to check whether an application is capable of displaying and handling different formats according to a specific region. This testing is categorized into multiple types depending upon the format being tested:
- Currency Format Testing: - This is done to check whether the application displays the correct format of currency e.g. an application must not display the currency in Dollars if it is used in Pakistan.
- Date Format Testing: - This testing ensures that the application displays the correct format of date and time according to the region it is being used in. Some countries use MM/DD/YYYY format while some use DD/MM/YYYY format. Hence, this testing analyzes whether an application can support multiple formats of date and time (24 hours format and 12 hours format).
- Zip-code Format Testing: - In this testing, the capability of the application to support different zip-code formats is checked. Some countries use numeric zip-code format while some use alpha-numeric format (e.g. Canada). Therefore, globalized software must support all formats of zip codes.
- Image Format Testing: - Different countries have different policies regarding the content displayed or broadcasted. Some countries like the theocratic states may deem certain images to be inappropriate. Therefore, global software must display or exclude images according to the country it is being used in. This is ensured in Image Format Testing.
Phases of Globalization Testing
Globalization Testing is executed in a systematic way. It comprises multiple phases and the software that is being subjected to globalization testing undergoes these phases sequentially:
Shaping the strategy: In this phase, the areas where the application is desired to be launched are identified.
Designing the Tests: At this stage, all the necessary data about the areas where the application is aimed to be launched is collected.
Setting up the testing environment: When all the necessary data about the areas is collected, then an environment for testing the application is created. The environment created is strictly according to the data collected about the locales. The environment is created by a common server containing multiple clients.
Executing the test: The application is eventually subjected to testing in the testing environment, which is an ideal environment to test different products without any biases.
Producing the summary: A summary about the performance of the application in the testing environment is produced. This is the last phase of this form of testing.
Benefits of Globalization Testing
- Aids in creating applications apt for the global market
- Enhances the quality and performance of the application
- Helps brands to retain their value
- Ensures that an application can be used across the globe
Keynote:
Globalization Testing is the need of the hour as the demand for globalized software is increasing unceasingly. It is highly improbable to develop quality globalized products without globalization testing. The Internationalization Testing and the Localization Testing (types of Globalization Testing) ensure that an application is perfectly compatible with a local region as well as with the international regions.
If you’re planning to establish a globalized software, contact an established QA testing team to get over the line.
Don't hire us right away
talk to our experts first,
Share your challenges, & then decide if we're the right fit for you! Talk to Us
Partnerships & Recognition
Commitment to excellence






